Resources
Resources
resources

Ring rolling begins with a circular shape which has been forged using a compression die and pierced to make a hollow ring.
(Scroll down to learn more)
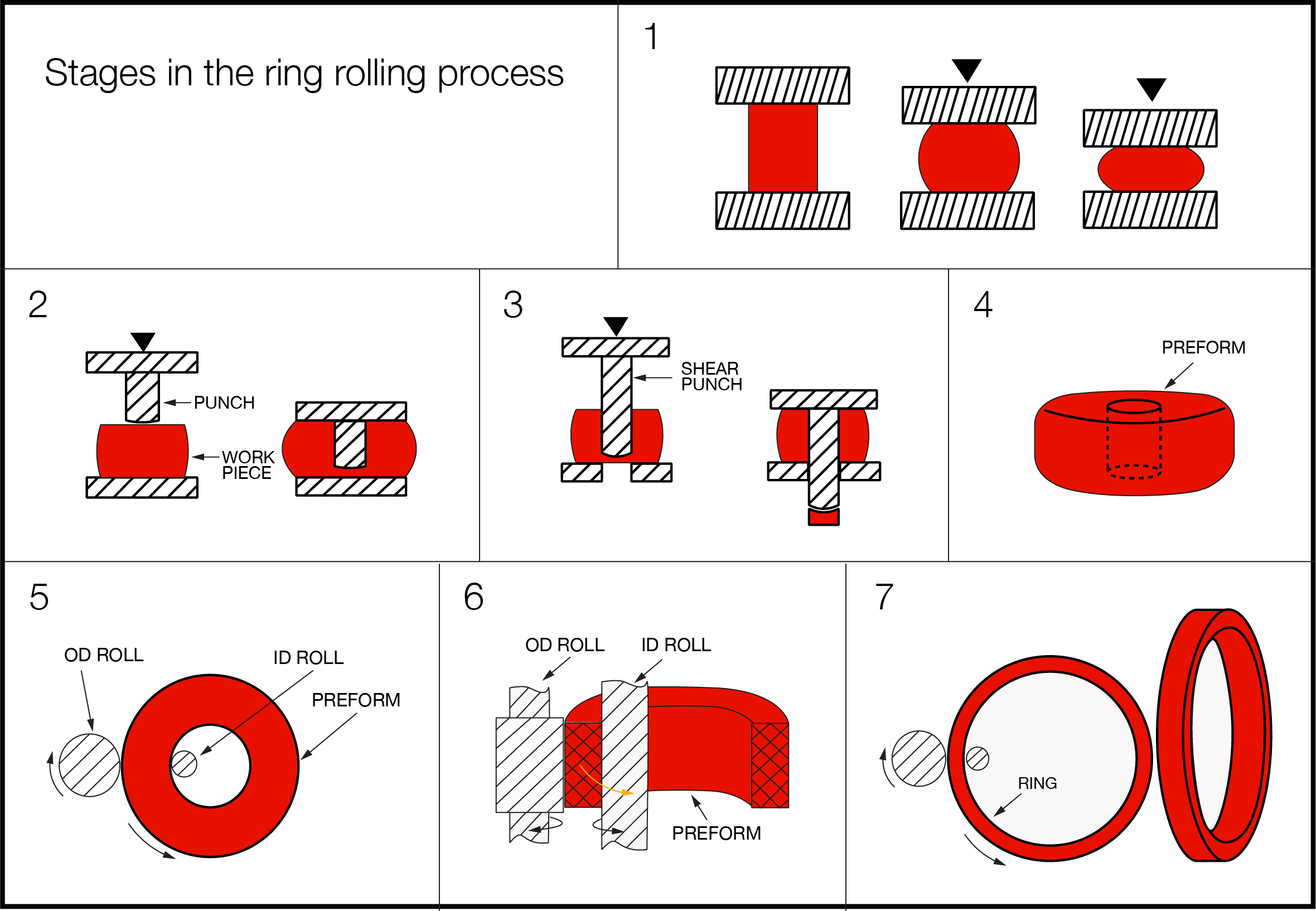
This piece is reheated and placed on a rolling mill and is rotated repeatedly. Applying pressure while the piece is in rotation reduces the cross-sectional area and expands the inner and outer diameters making a seamless rolled ring.
There are numerous ring rolling methods and equipment available that all yield a similar product. The average rolling mills are either horizontal or vertical and can produce a variety of ring sizes with outside diameters of up to 9.5 meters and weights of up to 65 tons. The shape of the rings ranges from flat, washer like shapes to big cylindrical shapes. Most commonly used is a rectangular, cross-section ring.
Download print version
The content of this page was curated for the distribution of industry related information from the Forging Industry Association and/or the American Foundry Society in reference to specific metallurgical processes.
Downloads
Company & Capabilities
Industries
Components
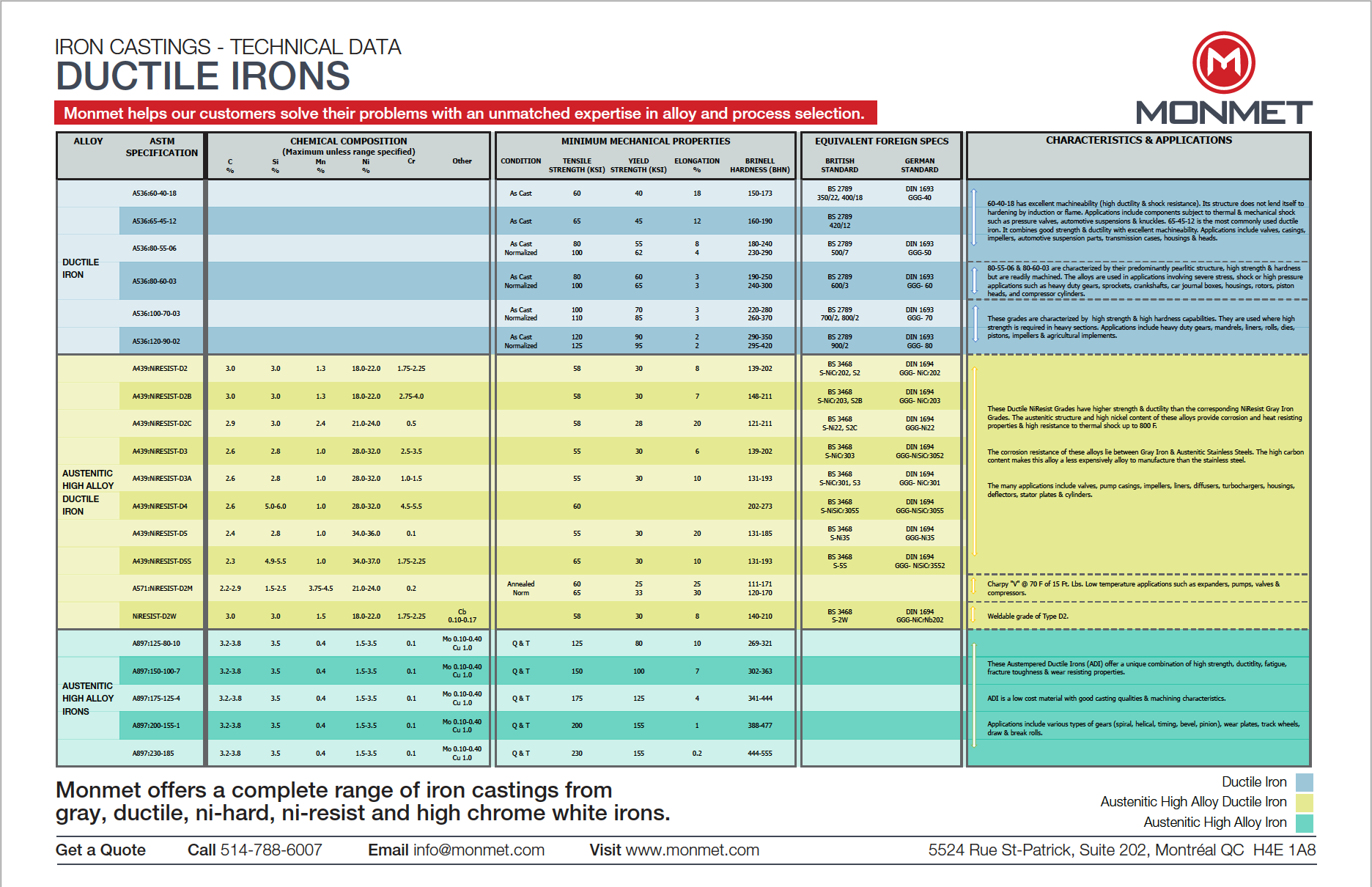
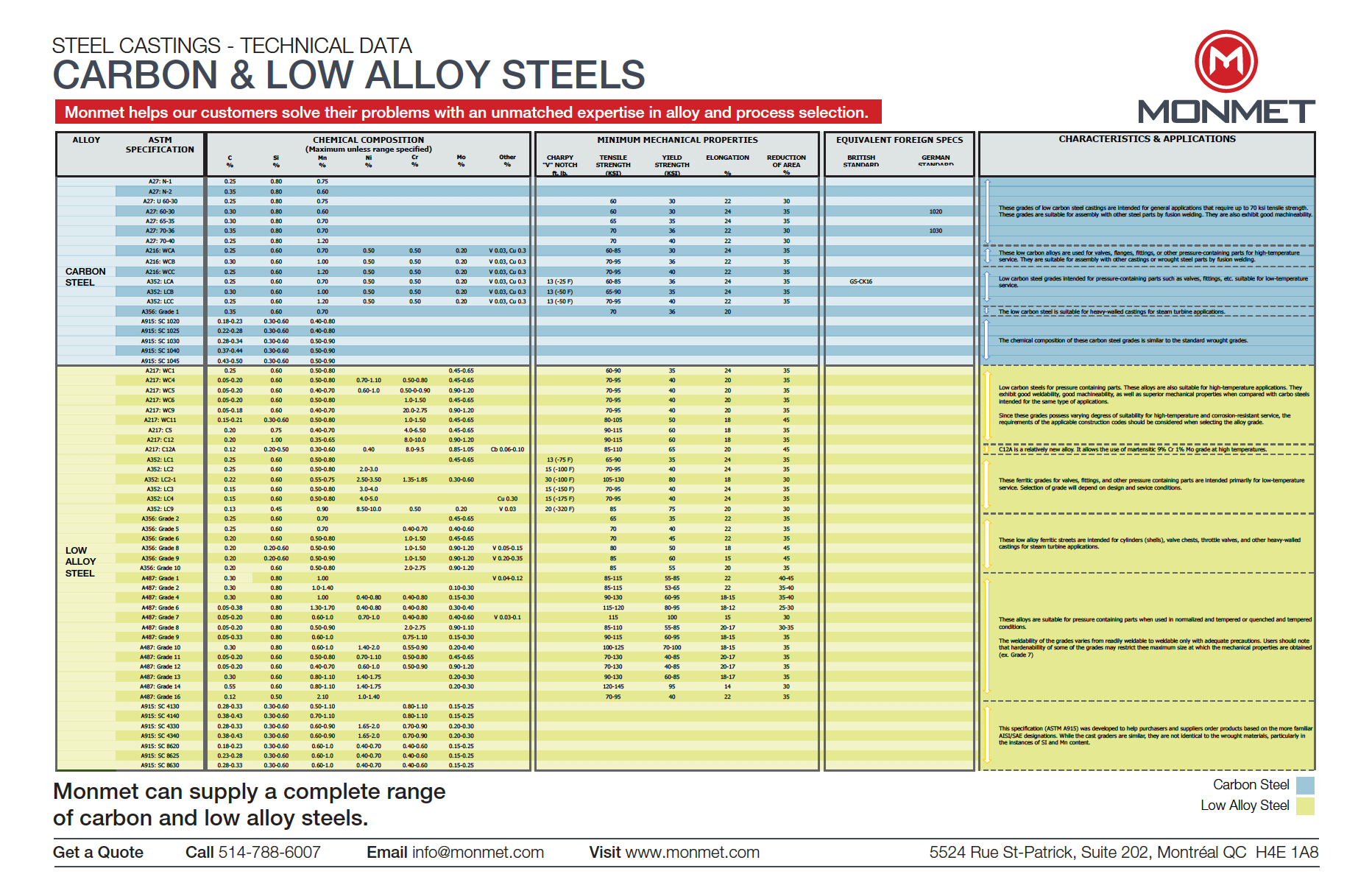
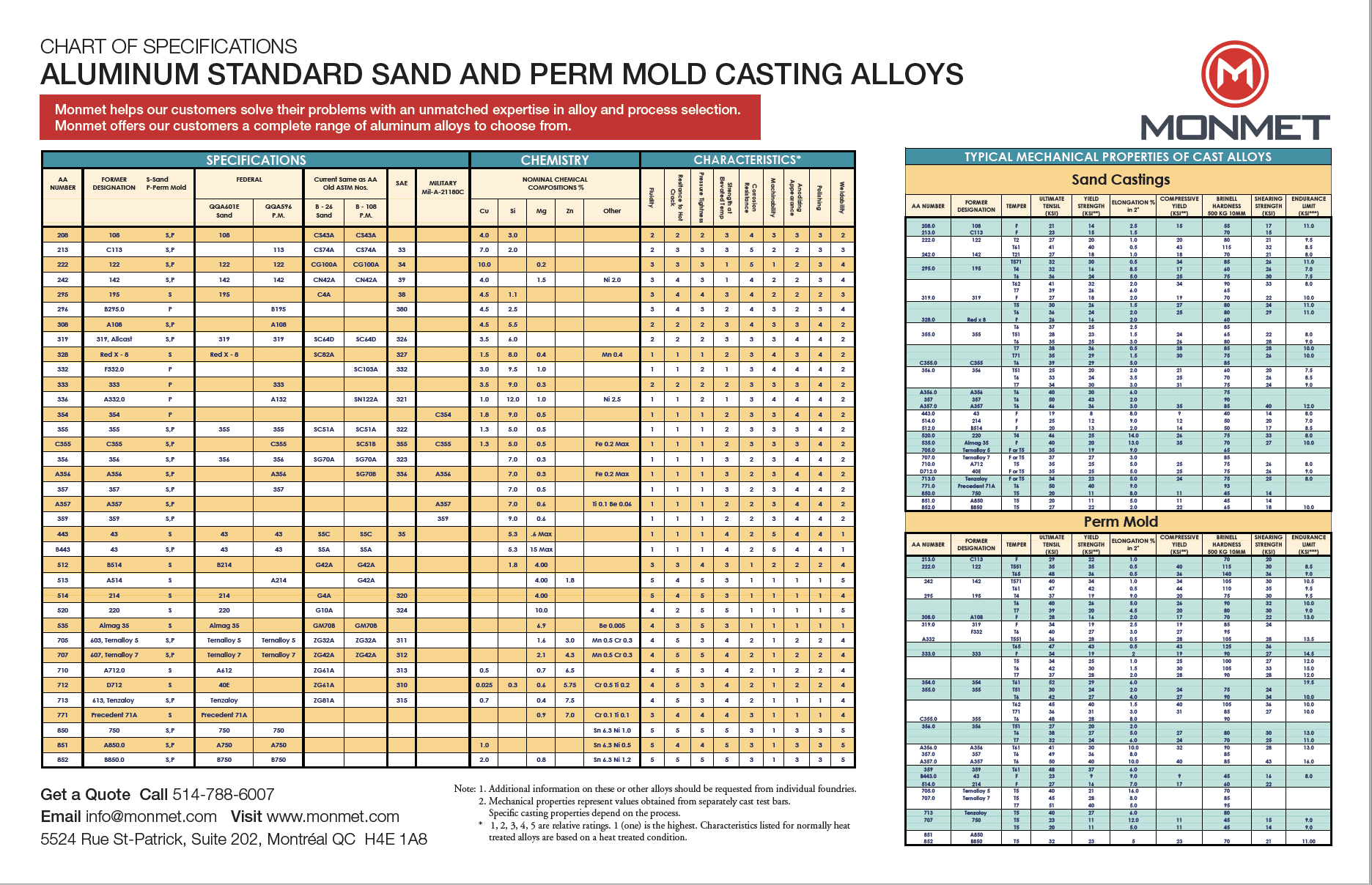
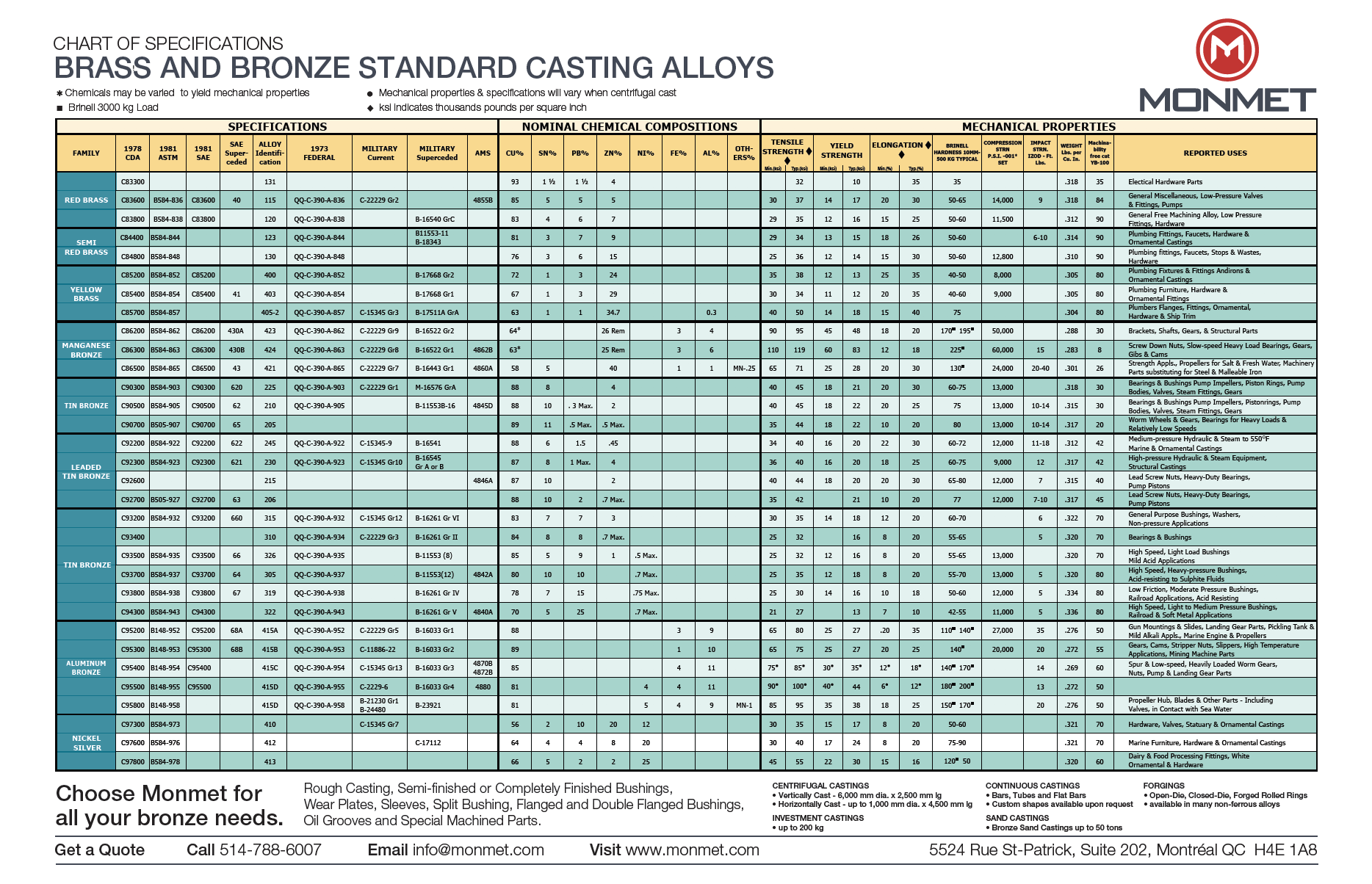
Technical Data
Learn Casting Processes
Sand Casting
Investment Casting
Centrifugal Casting
Continuous Casting
Learn Forging Processes
Open-Die Forging
Closed-Die Forging
Ring Rolling